Learn more about EK products
Visit EK Shop
Browse our high performance Quantum, Lignum and Classic product lines, Kits and Accessories.
Fluid Gaming Prebuilt PCs
Not the DIY person? Check out our fully water-cooled prebuilt PCs.
This website uses cookies. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy. By clicking “Accept All”, you agree to the storing of all cookies on your device. To learn more about our Cookie Policy and how to manage cookies, click here.
If you have read our initial blog What is PWM and how does it work?, then we can expand that topic with some tips and tricks. As we said before, the cool thing about PWM regulation is that you can use one PWM signal to govern all of your fans. So why not use the PWM signal from a GPU to do that?

Every modern gaming rig is more dependent on the GPU than the CPU. Every gaming oriented GPU that can handle most of the mainstream games produces roughly two to three times the amount of heat of an average Intel® Core™ i5 processor (which is plenty for mainstream gaming).
The EK-Cable PWM Predator Fan Adapter for GPU is a special adapter cable made for our EK-XLC Predator units.
You can replace the original PWM and tachometric signal cable on your Predator and use this one instead. You will be able to let the PWM profile of the graphics card control the speed of the fan on your EK-XLC Predator unit. Of course, this makes sense only if you have a liquid cooled GPU added to your Predator loop.
Our story of PWM does not end here. The same can be done with our EK-Cable PWM Fan Adapter for GPU.
With this adapter cable, you can directly attach any regular 4-pin PWM fan to the GPU 4-pin header or a chain of fans. If you have a computer that is performing GPU intensive tasks, or you have a separate loop to cool your GPU or multi-GPU setup, you can use the PWM signal from the graphics card(s) to control the speed of the fans.
Cryptocurrency miners are well aware of this little adapter cable since there were some GPUs that refused to mine if the card had no feedback from the spinning fans. Since every liquid cooled GPU has no fans running on it, this was a problem.
Be aware that the power limitation of the fan connector found on modern graphics cards is limited to 2 amperes! This means that if the 4-pin header on the graphics card delivers 2 amperes, it can handle up to four EK-Furious Vardar FF5-120 fans, ten EK-Vardar F4-120ER fans or even more F3, F2 or F1 Vardar fans. Just pay attention that not all fans on the market are so power efficient as the EK Vardar fans. There are examples where a single 120mm fan can draw 0.6A – 7.2W, which is more than three times of the EK-Vardar F4-120ER power consumption.
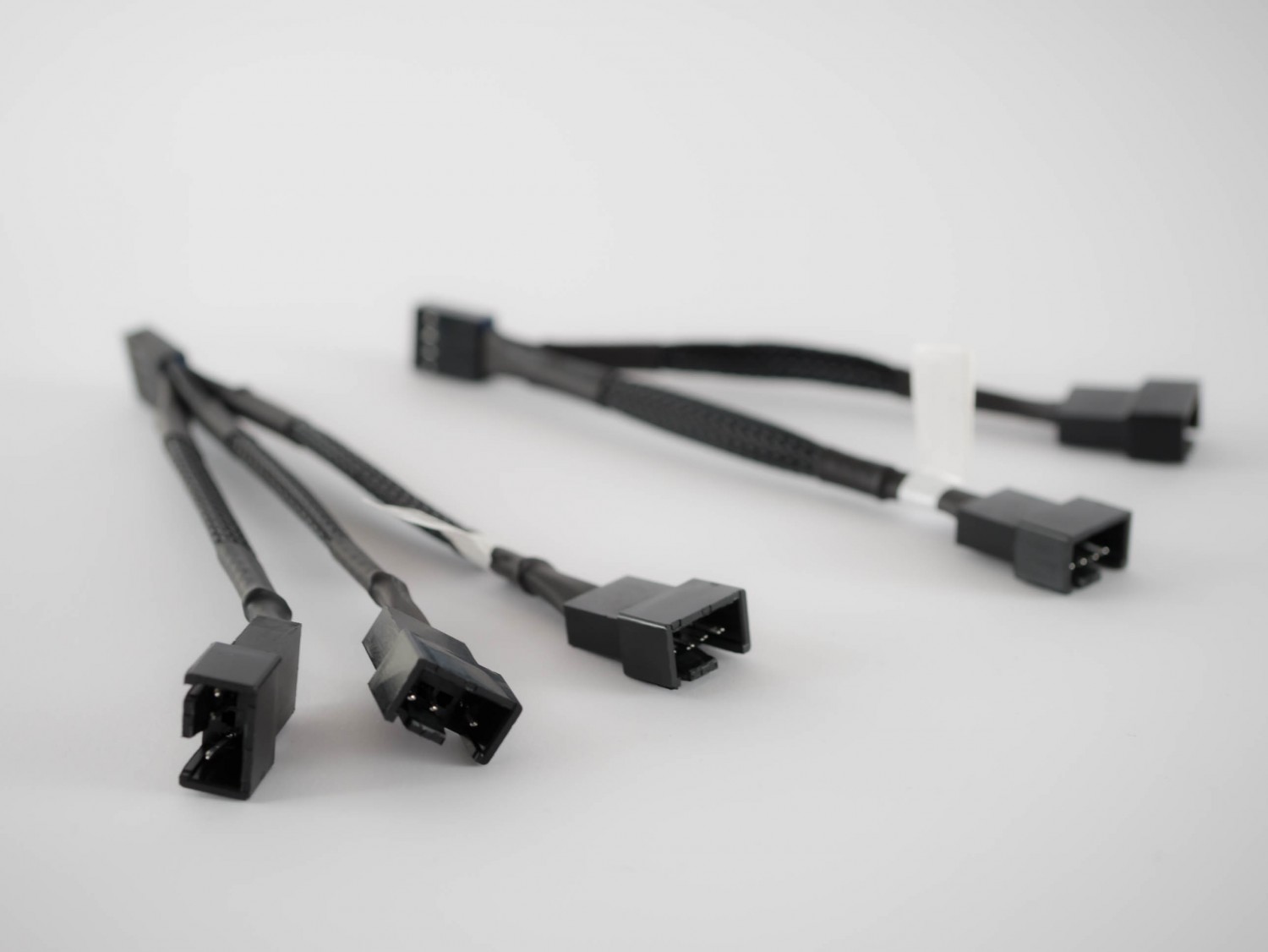
Moving on to some more of the PWM magic. We have the EK-Cable Y-Splitter 2-Fan PWM and the EK-Cable Y-Splitter 3-Fan PWM adapters. These are ordinary splitters for 4-pin fans, with only one header having the tachometric signal, since the motherboard can read the speed from only one fan at the time.

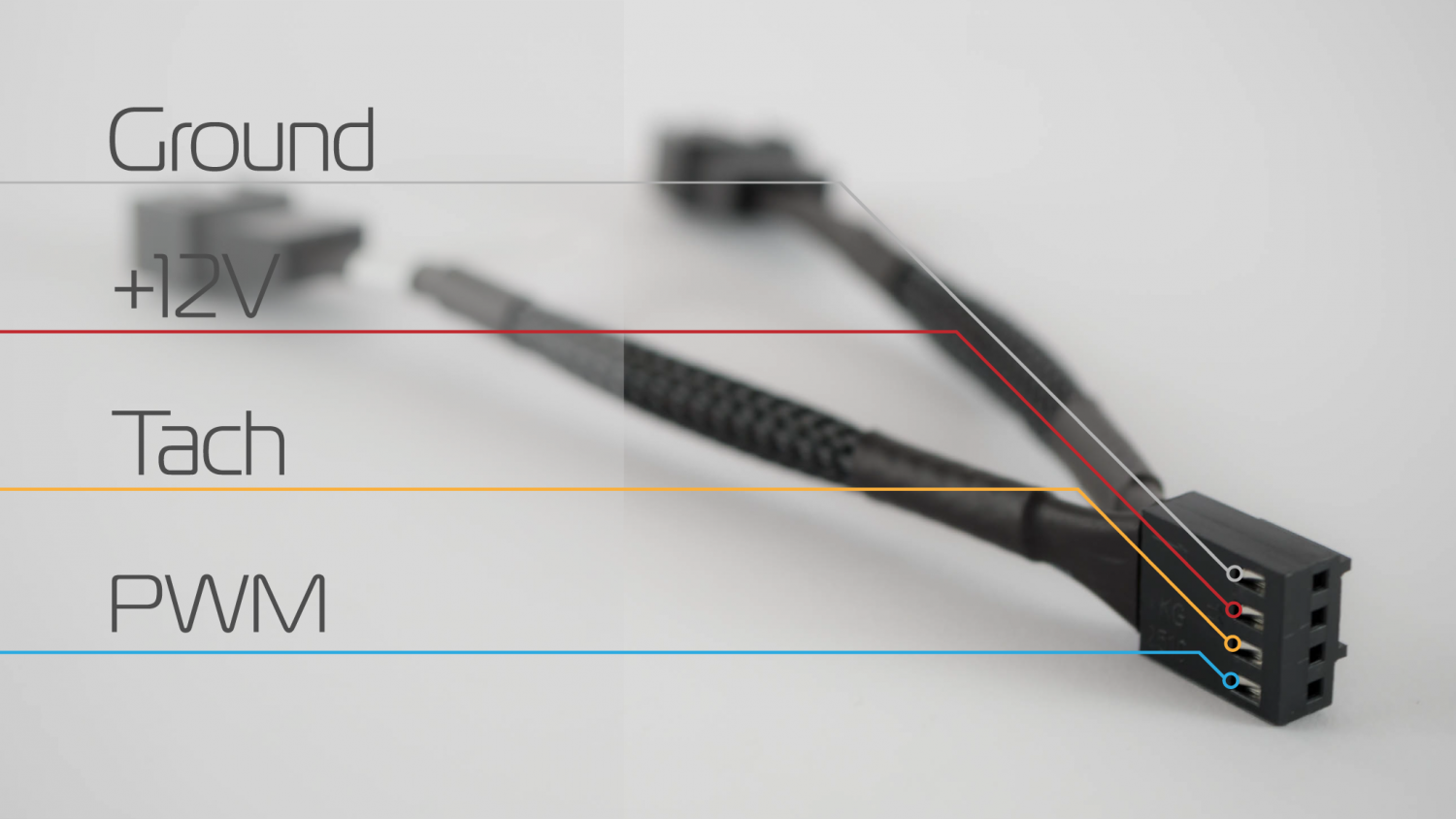

Most motherboard PWM headers can provide 1 ampere and they all work on 12V. If you know the power consumption or current of a fan, you can calculate the maximum number of fans you can attach to the fan header with the following formulas:
I(A) = P(W) / V(V)
P(W) = V(V) × I(A)
With I being the current expressed in Amperes, P the power expressed in Watts, and voltage expressed in Volts.

The safest way to run multiple fans on one source of PWM signal is the EK-Cable Splitter 4-Fan PWM Extended adapter. Since this adapter draws power out of a molex connector – directly from the power supply – there is no fear of overloading some 4-pin PWM headers on your motherboard or graphics card. This 4-way PWM splitter cable can be safely daisy-chained with any of the 2-way or 3-way PWM Y-splitters. You can also combine this 4-way PWM splitter with the PWM GPU Fan adapter, so that all of your fans are directed by the PWM profile of the graphics card.
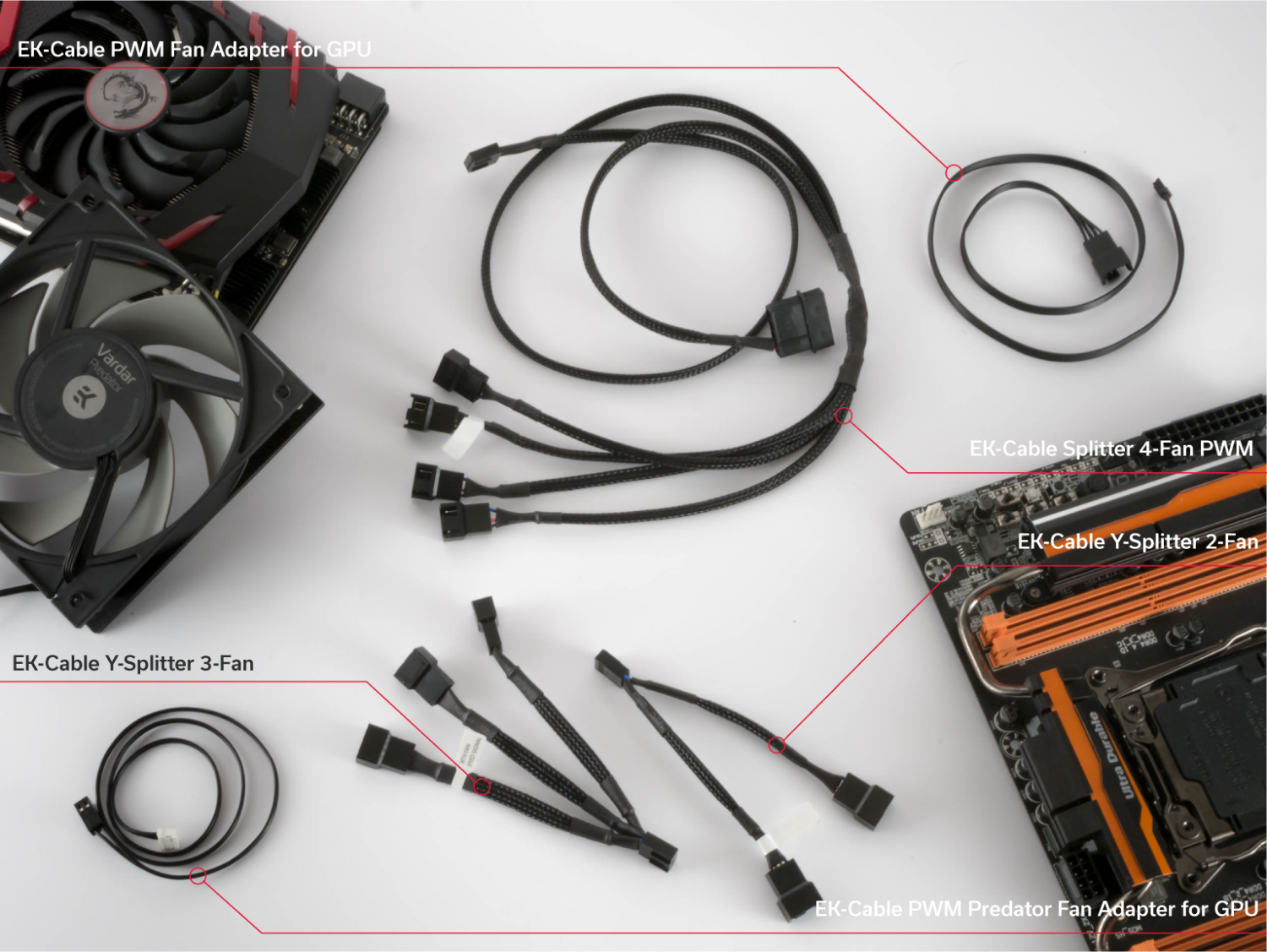

So why would you have the interest in any of these adapters? For reasons of silent computing and proper cooling management. And if you need help with some cables and various adapter solutions, be sure to check out our Power Cables & Adapters tab under the Accessories section!
Browse our high performance Quantum, Lignum and Classic product lines, Kits and Accessories.
Not the DIY person? Check out our fully water-cooled prebuilt PCs.



 PCAXE by Attila Gobor
PCAXE by Attila Gobor 